Description
304 Stainless Steel Pipe
304 stainless steel pipe is a versatile stainless steel that is widely used in the manufacture of equipment and equipment that require good overall performance (corrosion resistance and molding).Stainless steel 304 is a brand of stainless steel manufactured according to the ASTM standard, the equivalent of 0Cr19Ni9 ( 0Cr18Ni9 ) stainless steel, contains ≥18% of chromium and ≥8% nickel.
Ss 304 is the most widely used stainless steel, heat resistant steel, practical steel, Chinese steel. Used for food production equipment, common chemical equipment, nuclear energy, etc.
CHINESE NAME:304 Stainless Steel Pipe APPLICATIONS:SHIPBUIDING,OFFSHORE,CHEMICAL INDUSTRY,ETC
INTERNATIONAL NAME:TP 304 Stainless Steel Pipe SHAPE: ROUND,SQUARE,RECTANGULAR,HEX.
PERFORMANCE:STAINLESS METERIAL:TP304, SS304, AISI304, 1.4301, 304 STAINLESS STEEL 304
Ss304 / TP304 Stainless Steel Pipe 304 ECONNOMIC ROLE
TP 304/ Ss304 Stainless steel seamless pipe export is an important part of China’s export economy, it plays an important role in stimulating China’s economic growth, however, China’s foreign trade of stainless steel, stainless steel of China’s export met great resistance.
The TP 304/ Ss304 stainless steel pipe is used as a stainless steel tube and is used for the use of food equipment, general chemical equipment and equipment for the atomic energy industry.
The stainless steel rust resistance is stronger than the stainless steel materials of the 200 series. It is also good for high temperature, which can be up to 1000-1200 degrees. TP304/SS304 stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and good corrosion resistance.
304 stainless steel material has a strong resistance to corrosion in nitric acid, which is below the boiling temperature of less than 65%. Alkaline solution and most organic acids and inorganic acids also have good corrosion resistance.
Tp304/ ss304 Stainless Steel Pipe Od Tolerence.
| TOLERANCE GRADE | OD TOLERACE |
| D1 | ±1.5%,MIN ±0.75 mm |
| D2 | ±1.0%。MIN ±0.50 mm |
| D3 | ±0.75%.MIN ±0.30 mm |
| D4 | ±0.50%。MIN ±0.10 mm |
ASTM A312 TP304/ Ss304 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe / Welded Pipe CACULATOR:(OD-W)*W*0.02491=KG/METER OD=OUT DIAMETER W=WALL THICKNESS
TP304 / Ss304 304 Stainless Steel Pipe DETAILED INTRODUCTION:
Products according to ASTM A312 / ASTM A213 / ASTM A269/ASTM A511/ASTM A249/ASTM A554/GIS G3459/EN10216-5
( fluid conveying stainless steel seamless steel tube ) stainless steel seamless tube ( boiler, stainless steel seamless steel tubes for heat exchanger ),
decorative welded stainless steel pipe ,
building decorative stainless steel welded pipe ( JG/T 3030-1995 ),
all pass strict examination, conform to the requirements of the national standard specifications material 321/1 304/
Mechanical properties of tp304/ss304 stainless steel seamless pipe:
| grade | y.sσb/MPa | t.sδ5(%) |
| tp304/ss304 | ≥450 | ≥40 |
| tp321 | ≥560 | ≥40 |
| tp316l | ≥490 | ≥40 |
| tp347h | ≥550 | ≥35 |
| s31803/2205 | ≥550 | ≥35 |
304 Stainless Steel Pipe Advantages:Comparative Analysis of TP304, SS304 & AISI304
1. Material Standards & Composition
TP304 (ASTM/ASME), SS304 (JIS SUS304), and AISI304 (SAE 304) are interchangeable grades with minor regional certification variations. All three share a base composition of 18–20% Cr and 8–12% Ni, ensuring oxidation resistance and ductility. Carbon content is strictly controlled (≤0.08% for TP304/AISI304; ≤0.07% for SS304) to minimize carbide precipitation during welding.
Table 1: Chemical Composition Comparison
| Grade | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | C (%) | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP304 | 18–20 | 8–11 | ≤0.08 | ASTM A312/A213/A269/A554/A249/A511 |
| SS304 | 18–20 | 8–10.5 | ≤0.07 | JIS G3459 |
| AISI304 | 18–20 | 8–10.5 | ≤0.08 | AISI (legacy) |
PMI Tested Actual Chemical :

TP304, SS304, AISI304, 1.4301, 304 STAINLESS STEEL PIPE MANUFACTURER & SUPPLIER IN CHINA, CONTACT US TO GET DISCOUTED PRICE AND HIGH QUALITY STAINLESS STEEL 304 PIPE.
2. Mechanical & Thermal Performance
All grades exhibit ≥520 MPa tensile strength and ≥205 MPa yield strength, suitable for high-pressure piping system. SS304 shows marginally higher elongation (≥40%) due to JIS-standardized processing. Thermal stability extends to 800°C, ideal for heat exchangers and exhaust components.
Figure 1: Yield Strength vs. Temperature
![Yield strength retention up to 500°C]
3. Key Advantages
① Corrosion Resistance
Chromium oxide passivation layers provide immunity to oxidation, weak acids, and organic compounds12. All grades resist stress corrosion cracking in chloride-free environments. For marine applications, TP304L (C≤0.03%) is recommended.
② Formability & Weldability
Cold/hot working (e.g., bending, stamping) is feasible without cracking16. TIG/MIG welding produces defect-free joints, maintaining corrosion resistance post-welding.
③ Hygienic Properties
Electropolished surfaces inhibit bacterial growth, critical for food processing and pharmaceutical pipelines.
④ Cost Efficiency
SS304 costs 5–8% less than TP304 due to Japan’s centralized production. AISI304 remains economical for low-pressure industrial components.
4. Application Scenarios
| Industry | Preferred Grade | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | TP304 | Acid transport pipelines |
| Construction | SS304 | Structural supports |
| Food & Beverage | AISI304/TP304 | Sanitary tubing |
| Oil & Gas | TP304 | High-pressure manifolds |
5. Limitations & Alternatives
Chloride exposure (>50 ppm) causes pitting corrosion; switch to 316L for marine use.
Reducing acids (e.g., sulfuric acid) require duplex stainless steels.
Conclusion
TP304, SS304, and AISI304 stainless steel pipes deliver interchangeable performance with region-specific certification advantages. Their balanced strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability make them indispensable across industries. For ASTM-compliant projects, prioritize TP304; for cost-sensitive JIS applications, SS304 excels
TP304/ Ss304 Stainless Steel 304 Pipe Excutive Standard:
For 304 stainless steel, the Ni element in its composition is very important, which directly determines the corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel and its value.
The most important elements in 304 are Ni and Cr, but they are not limited to these two elements.
Specific requirements are specified by product standards. The common judgment in the industry is that as long as the Ni content is greater than 8% and the Cr content is greater than 18%, it can be considered as 304 stainless steel.
This is why the industry calls this type of stainless steel 18/8 stainless steel.
In fact, the relevant product standards have very clear regulations for 304, and these product standards have some differences for different shapes of stainless steel.
Below are some common product standards and tests.
To determine whether a material is 304 stainless steel, it must meet the requirements of each element in the product standard. As long as one does not meet the requirements, it cannot be called 304 stainless steel.
1、ASTM A312(Standard Chemical Compositon for Stainless Steel Pipe And Tubes)
304 | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni |
require,% | ≤0.08 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | ≤1.00 | 18.0–20.0 | 8.0-11.0 |
2、ASTM A269/ASTM A213(Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Tubing for Pressure essels and for General Applications)
304 | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | N |
require,% | ≤0.07 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.75 | 17.5–19.5 | 8.0–10.5 | ≤0.10 |
Perfect Job Finshed OEM Service for Mexico Client’s ASTM A213 TP304 Stainless Steel Seamless Tube With od19.05mm*2.11mm*11278mm length.
3、EN 10216-5(cold-finished 1.4301 stainless steel pipe and tubes)
1.4301/SS304 | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni |
require,% | ≤0.08 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | ≤1.00 | 18.0–20.0 | 8.0-10.5 |
4、JIS G3459 (SUS 304 Stainless Steel Pipe)
SUS 304 | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni |
require,% | ≤0.08 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | ≤1.00 | 18.0–20.0 | 8.0-10.5 |
The above four standards are just a few common standards. In fact, there are more than these standards mentioned in ASTM and JIS 304.
In fact, each standard has different requirements for 304, so to determine whether a material is 304, the accurate expression should be whether it meets the 304 requirements in a product standard.
The material certificate generally needs to issue the following types of reports: detailed standard specification comparison: as of 2025-02-08
No. | Standard / S30400 | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | N | Cu |
1 | ASTM A276/A276M-15 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
2 | ASTM A959-11 | 0.07 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 17.5-19.5 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
3 | ASTM A240/A240M-15a | 0.07 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 0.75 | 17.5-19.5 | 8.0-10.5 | ||
4 | ASTM A182/A182M-15 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | 0.10 | |
5 | ASTM A193/A193M-15 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
6 | ASTM A269/A269M-15 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
7 | ASTM A312/A312M-15a | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
8 | ASTM A320/A320M-15a | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
9 | ASTM A403/A403M-15 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
10 | ASTM A493-09(2013) | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
11 | ASTM A554-15a (MT-304) | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | ||
12 | JIS G4303:2012 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | ||
13 | JIS G4304:2012 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | ||
14 | JIS G4305:2012 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | ||
15 | GB/T 20878-2007 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 |
Tp304 / SS304 AISI304 Stainless Steel Pipe 304 PRODCUTION PROCESS
COLD DRAWN ( TP304 / SS 304 304 Stainless Steel Pipe seamless pipe) :
The tp304 / ss 304 stainless steel seamless pipe is a brand of stainless steel manufactured according to the ASTM standard, 304 stainless steel pipe are equivalent to China’s 0Cr19Ni9 (0Cr18Ni9) stainless steel pipe. 304 contains 18% of chromium and 8% nickel.
304 is the most widely used for stainless steel, the equipment for food, general chemical equipment, and the atomic energy industry.
SS 304 is a versatile stainless steel tube that is widely used to make equipment and parts that require good overall performance (corrosion resistance and molding).
304 is the most widely used stainless steel, heat resistant steel. Used in food production equipment, chemical equipment, nuclear power, etc.
tp304 / ss304 stainless steel pipe chemical composition specification C Si Mn P S Cr Ni (nickel) Mo
SUS304 less than or less than 0.08 is less than or equal to 1.00 or less than 0.03, or less than 0.05, 0.03, 18.00-20.00, 8.25 ~ 10.50
Classification of TP304/SS 304 stainless steel pipe has a lot of kinds, the first is the seamless pipe and ERW EFW pipe,
the second is the most basic classification structure with TP304/SS 304 stainless steel pipe and industrial fluid with TP304/SS 304 stainless steel pipe.
There is also a division of the national, Japanese and American standard
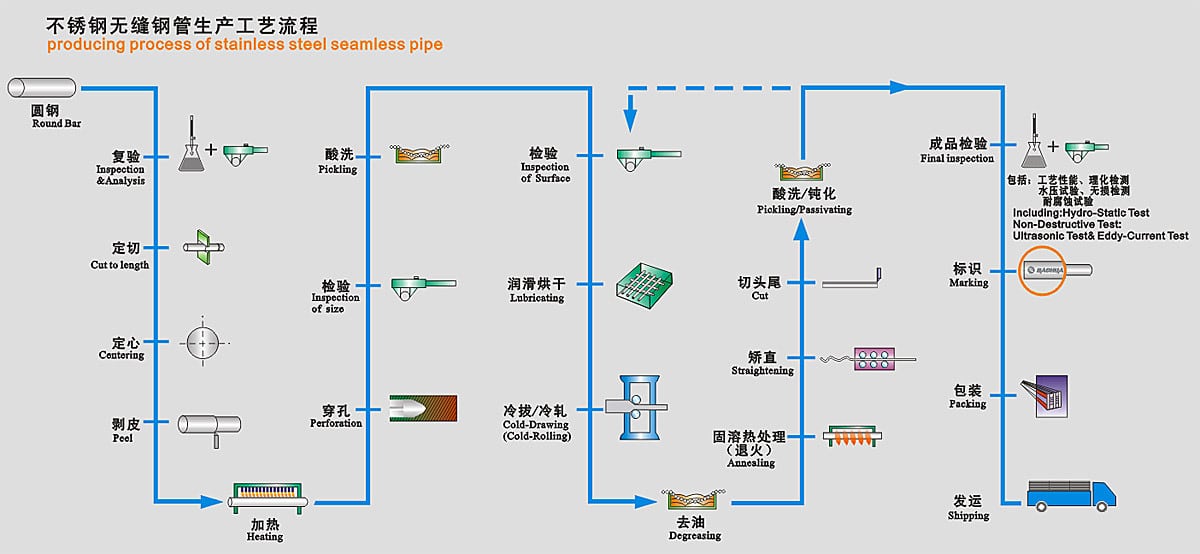
SS304/TP304 /AISI304S/SUS304/1.4301/ 304 stainless steel seamless pipe illustrative flow chart detailing the production stages, quality control, and industrial applications of corrosion-resistant stainless steel seamless pipes in fluid transportation systems.
TP304 / Ss304 304 Stainless Steel Seamless & Welded Pipe In Stock With Size Table.
1/2”-16” SCH10 40 80
analysis of performance:
TP304 / SS 304 stainless steel pipe has good corrosion resistance, excellent corrosion performance and cold processing and stamping performance, which can be used as a heat-resistant stainless steel.
At the same time, the steel – 180 ℃ under the condition of the mechanical properties of this dismal disease.
The plastic, toughness and cold processing of steel in solid solution are good. The production and usage of 304 stainless steel are the largest and the most widely used steel types, which are resistant to corrosion in dielectric acid and atmosphere and water.
TP304 / SS304 stainless steel has a good cold and hot working performance, can be in all kinds of cold and hot working process,Heat treatment process
304 stainless steel pipe with solid solution treatment temperature of 1080-1100 ℃, cooling water or air cooling, Cold intermediate annealing temperature more than in 850-970 ℃, heat preservation water after a certain time.
After the solid solution, the tissue of the steel is the austenitic tissue, and sometimes there is a small amount of ferrite.
TP304 / SS304 stainless steel thin plate is used in the application process, often used in cold molding operation. Its cold molding performance is an important technical index to measure the success of the molding and yield.

TP304, SS304, AISI304, 1.4301, 304 STAINLESS STEEL PIPE SUPPLIER & MANUFACTURER IN CHINA, CONTACT US TO GET DISCOUTED PRICE & HIGH QUALITY STAINLESS STEEL 304 PIPES IN STOCK.
| Dimensions for ASME/ANSI Standards | Unit:mm | ||||||||||||
| B16.9 B16.28 B36.10 | |||||||||||||
| Nominal pipe Size(NPS) | Outside Diameter | Nominal Wall Thickness | |||||||||||
| Sch5s | SCH10S | Sch20 | Sch30 | Sch40 | STD | Sch80 | XS | Sch160 | XXS | ||||
| 8 | 1/4 | 13.7 | 0.54 | – | 1.65 | – | 1.85 | 2.24 | 2.24 | 3.02 | 3.02 | – | – |
| 10 | 3/8 | 17.1 | 0.675 | – | 1.65 | – | 1.85 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 3.20 | 3.20 | – | – |
| 15 | 1/2 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 1.65 | 2.11 | – | 2.41 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 3.73 | 3.73 | 4.78 | 7.47 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 26.7 | 1.05 | 1.65 | 2.11 | – | 2.41 | 2.87 | 2.87 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.56 | 7.82 |
| 25 | 1 | 33.4 | 1.32 | 1.65 | 2.77 | – | 2.90 | 3.38 | 3.38 | 4.55 | 4.55 | 6.35 | 9.09 |
| 32 | 1.1/4 | 42.2 | 1.66 | 1.65 | 2.77 | – | 2.97 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 4.85 | 4.85 | 6.35 | 9.70 |
| 40 | 1.1/2 | 48.3 | 1.90 | 1.65 | 2.77 | – | 3.18 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 5.08 | 5.08 | 7.14 | 10.15 |
| 50 | 2 | 60.3 | 2.38 | 1.65 | 2.77 | – | 3.18 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.54 | 5.54 | 8.74 | 11.07 |
| 65 | 2.1/2 | 73.0 | 2.88 | 2.11 | 3.05 | – | 4.78 | 5.16 | 5.16 | 7.01 | 7.01 | 9.53 | 14.02 |
| 80 | 3 | 88.9 | 3.50 | 2.11 | 3.05 | – | 4.78 | 5.49 | 5.49 | 7.62 | 7.62 | 11.13 | 15.24 |
| 90 | 3.1/2 | 101.6 | 4.00 | 2.11 | 3.05 | – | 4.78 | 5.74 | 5.74 | 8.08 | 8.08 | – | – |
| 100 | 4 | 114.3 | 4.50 | 2.11 | 3.05 | – | 4.78 | 6.02 | 6.02 | 8.56 | 8.56 | 13.49 | 17.12 |
| 125 | 5 | 141.3 | 5.56 | 2.77 | 3.40 | – | – | 6.55 | 6.55 | 9.53 | 9.53 | 15.88 | 19.05 |
| 150 | 6 | 168.3 | 6.62 | 2.77 | 3.40 | – | – | 7.11 | 7.11 | 10.97 | 10.97 | 18.26 | 21.96 |
| 200 | 8 | 219.1 | 8.62 | 2.77 | 3.76 | 6.35 | 7.04 | 8.18 | 8.18 | 12.70 | 12.70 | 23.01 | 22.23 |
| 250 | 10 | 273.0 | 10.75 | 3.40 | 4.19 | 6.35 | 7.80 | 9.27 | 9.27 | 15.09 | 12.70 | 28.58 | 25.40 |
| 300 | 12 | 323.8 | 12.75 | 3.96 | 4.57 | 6.35 | 8.38 | 10.13 | 9.53 | 17.48 | 12.70 | 33.32 | 25.40 |
| 350 | 14 | 355.6 | 14 | 3.96 | 4.78 | 7.92 | 9.53 | 11.13 | 9.53 | 19.05 | 12.70 | 35.71 | – |
| 400 | 16 | 406.4 | 16 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 7.92 | 9.53 | 12.70 | 9.53 | 21.44 | 12.70 | 40.49 | – |
| 450 | 18 | 457 | 18 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 7.92 | 11.13 | 14.27 | 9.53 | 23.83 | 12.70 | 45.24 | – |
| 500 | 10 | 508 | 20 | 4.78 | 5.54 | 9.53 | 12.70 | 15.09 | 9.53 | 26.19 | 12.70 | 50.01 | – |
| 550 | 22 | 559 | 22 | 4.78 | 5.54 | 9.53 | 12.70 | – | 9.53 | 28.58 | 12.70 | 53.98 | – |
| 600 | 24 | 610 | 24 | 5.54 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 14.27 | 17.48 | 9.53 | 30.96 | 12.70 | 59.54 | – |
| 650 | *26 | 660 | 26 | – | – | – | – | – | 9.53 | – | 12.70 | – | – |
| 700 | *28 | 711 | 28 | – | – | – | – | – | 9.53 | – | 12.70 | – | – |
| 750 | *30 | 762 | 30 | – | – | – | – | – | 9.53 | – | 12.70 | – | – |
| 800 | *32 | 813 | 32 | – | – | – | – | – | 9.53 | – | 12.70 | – | – |
304 Stainless Steel Pipe Applications:
1. SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY
2. CHEMICAL INDUSTRY
3. WATER INDUSTRY
4. STEEL INDSUTRY
5. POWER STATION INDUSTRY
6. OIL&GAS INDSUCTRY
7. MARINE INDUSTRY
8. OFFSHORE&ONSHORE INDSUTRY
9. USE IN FOOD INDUSTRY
10. USE IN MEICAL INDSTURY
Historical Evolution of 304 Stainless Steel Pipes: TP304, SS304 & AISI304
1. Origins of Stainless Steel
The invention of stainless steel traces back to 1916, when British metallurgist Harry Brearley discovered chromium-enhanced steel’s corrosion resistance while developing rifle barrels. This breakthrough laid the foundation for modern austenitic stainless steels like 30418. By the 1930s, the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) established standardized grading systems, including AISI 304 (18% Cr, 8% Ni).
2. Development of Regional Standards
AISI 304 stainless steel pipe
AISI 304 became the baseline for industrial applications, with its composition (18-20% Cr, 8-10.5% Ni) ensuring corrosion resistance and formability. Its legacy classification persists in non-piping contexts like architectural components.
TP304 stainless steel pipe
Introduced under ASTM A312/A213, TP304 emerged as the U.S. standard for piping systems, allowing slightly higher nickel (8-11%) for improved weldability in chemical processing.
SS304 stainless steel pipe
Japan’s JIS SUS304 (SS304) refined carbon control (≤0.07%) to minimize carbide precipitation in welded structures, prioritizing elongation (≥40%) for construction applications.
3. Key Milestones
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1916 | Brearley patents chromium steel, marking stainless steel’s birth |
| 1930 | AISI formalizes 304 series with 18/8 Cr/Ni ratios |
| 1950 | ASTM defines TP304 for high-temperature piping systems |
| 1980 | JIS SUS304 gains prominence in Asian construction projects |
4. Material Advancements
Chemical Composition
| Grade | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | C (%) | Key Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI304 | 18-20 | 8-10.5 | ≤0.08 | Universal industrial adoption |
| TP304 | 18-20 | 8-11 | ≤0.08 | Enhanced weldability |
| SS304 | 18-20 | 8-10.5 | ≤0.07 | Low-carbon JIS optimization |
Performance Enhancements
1950s: TP304’s ASTM certification enabled use in oil/gas pipelines (≤525°C).
2000s: SS304’s electropolishing improved hygiene for food/pharma industries.
5. Global Adoption
Global market share by region (2024 data)
Americas: TP304 dominates due to ASTM compliance in energy sectors.
Asia: SS304 accounts for 65% of construction projects (JIS G3459).
Europe: AISI 304 remains prevalent in legacy industrial systems.
6. Modern Challenges & Solutions
Chloride corrosion: TP304L (C≤0.03%) mitigates pitting in coastal environments.
Cost pressures: SS304’s centralized Japanese production reduces pricing by 5-8% vs. TP304.
Conclusion
From Brearley’s 1916 breakthrough to modern ASTM/ISO certifications, 304 stainless steel pipes (TP304, SS304, AISI304) have evolved through regional standardization and performance optimization. Their 18/8 Cr/Ni formula remains a benchmark for durability, corrosion resistance, and cross-industry versatility
Calculating Weight of 304 Stainless Steel Pipes: Formulas and Applications
304 stainless steel pipes (TP304, SS304, AISI 304) are widely used in industrial applications due to their corrosion resistance and durability. This article explains the weight calculation formulas for these grades and their regional compliance standards.
- Basic Weight Formula
The weight of a 304 stainless steel pipe is determined by its density (7.93 g/cm³) and geometric parameters. The universal formula is:
- OD: Outer diameter (mm)
- WT: Wall thickness (mm)
- L: Length (m)
This formula simplifies to 0.02491 × (OD – WT) × WT × L for quick estimation.
- Grade-Specific Applications
TP304 stainless steel pipe(ASTM A312): Dominant in the Americas for energy pipelines due to compliance with ASTM standards.
SS304 stainless steel pipe (JIS G3459): Preferred in Asian construction projects for its low-carbon formulation.
AISI 304 stainless steel pipe : Retains legacy use in European industrial systems due to compatibility with existing infrastructure.
- Calculation Example
For a stainless steel 304 pipe with OD = 100 mm, WT = 10 mm, and L = 6 m:
Weight=0.02491×(100−10)×10×6=134.5 kgs
- Key Influencing Factors
Wall Thickness: A 10% increase in WT raises weight by ~12%.
Length: Weight scales linearly with pipe length.
Density Variations: Minor deviations (e.g., 7.93–7.98 g/cm³) affect precision.
- Comparison Chart
Grade&Standard Typical Use Case Formula Adjustment
TP304&ASTM A312 High-pressure pipelines None
SS304&JIS G3459 Structural frameworks Lower carbon tolerance
AISI 304&EN 1.4301 Legacy chemical plants None
- Practical Considerations
Use laser measurement tools to ensure accurate OD and WT inputs.
For non-circular pipes (e.g., square or rectangular), adjust the formula using equivalent perimeter calculations.
Verify regional standards (e.g., ASTM vs. JIS) to align with material certifications.
This guide provides a foundation for calculating weights across TP304 stainless steel pipe, SS304 stainless steel pipe, and AISI 304 stainless steel pipes, ensuring compliance with global engineering requirements. For complex projects, consult ASTM or JIS documentation for grade-specific tolerances













